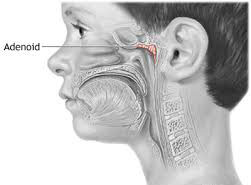
Adenoid removal, also called adenoidectomy, is a common surgery to remove the adenoids. The adenoids are glands located in the roof of the mouth, behind the soft palate where the nose connects to the throat.
The adenoids produce antibodies (white blood cells) that help fight infections. Typically, the adenoids shrink during adolescence and may disappear by adulthood.
Doctors often perform adenoid removals and tonsillectomies (removal of the tonsils) together. Chronic throat and respiratory infections often cause inflammation and infection in both glands.
Frequent throat infections can cause the adenoids to enlarge. Enlarged adenoids can obstruct breathing and block the Eustachian tubes, which connect your middle ear to the back of your nose. Clogged Eustachian tubes cause ear infections that can jeopardize your child’s hearing and respiratory health.
Swollen adenoids block the airways and can cause the following symptoms:
- frequent ear infections
- sore throat
- difficulty swallowing
- difficulty breathing through the nose
- habitual mouth breathing
- obstructive sleep apnea, which involves periodic lapses in breathing during sleep
Adenoid Removal
Your child’s doctor may recommend an adenoid removal if your child has chronic ear or throat infections that:
- don’t respond to antibiotic treatments
- occur more than 5 or 6 times per year
- impede your child’s education due to frequent absences
Dr. Ebrahim performs the Adenoidectomy under general anesthesia. This is usually done in an outpatient setting, which means that your child can go home on the day of the surgery.
The adenoids are usually removed through the mouth. Dr. Ebrahim will insert a small instrument into the mouth to prop it open. He’ll then remove the adenoids by making a small incision or by cauterizing, which involves sealing the area with a heated device.
Cauterizing and packing the area with absorbent material, such as gauze, will control bleeding during and after the procedure. Stitches aren’t usually necessary.
After the procedure, your child will stay in a recovery room until they wake up. You’ll receive medication to reduce pain and swelling. Complete recovery from an adenoidectomy usually takes one to two weeks.